Introduction: Vertigo vs Dizziness
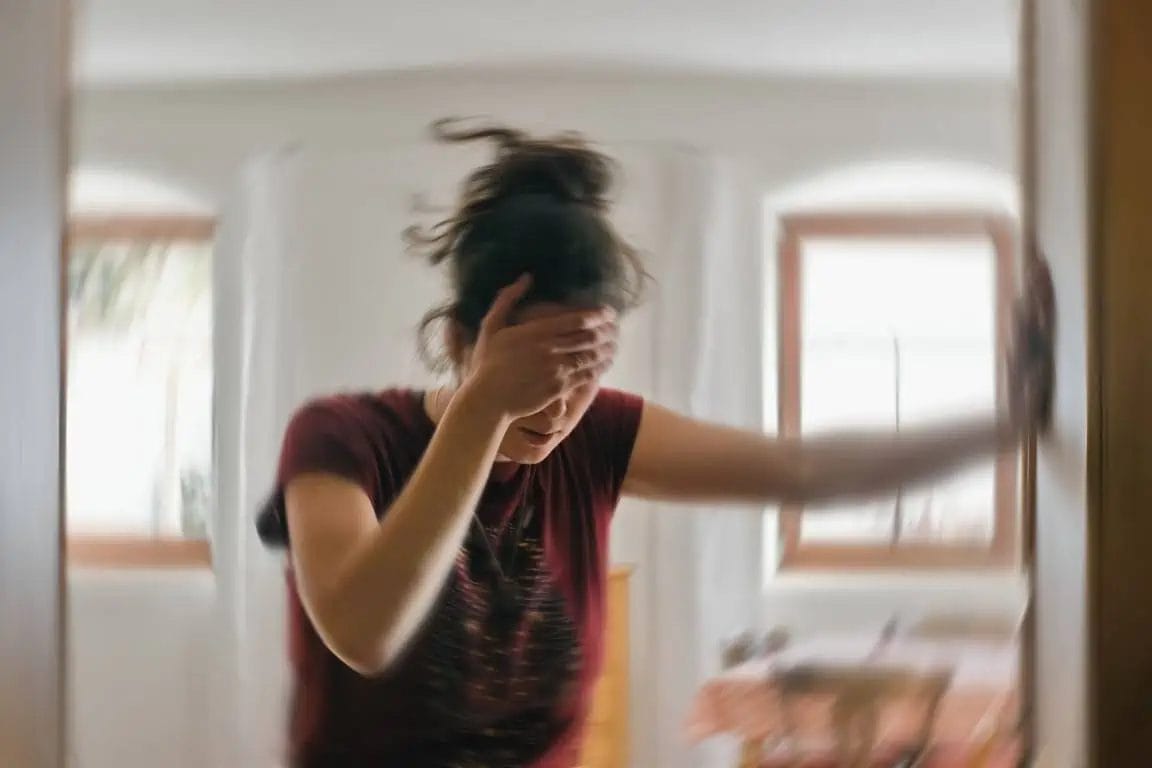
Vertigo, dizziness, and imbalance are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct symptoms with different underlying causes. It’s important to understand the differences to ensure proper diagnosis and effective treatment.
Vertigo is the sensation of spinning or whirling, often described as a feeling that the individual or the environment is moving. This sensation can be triggered by changes in head position or movement. Dizziness, on the other hand, is a more general term that encompasses a range of sensations, including lightheadedness, unsteadiness, and a feeling of being off-balance. Imbalance, or disequilibrium, refers to the difficulty in maintaining a stable and coordinated posture and gait.
While these symptoms may seem similar, they can have vastly different causes, ranging from inner ear disorders to neurological conditions. It’s crucial to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive the appropriate treatment. Treating vertigo, dizziness, or imbalance as a single disorder can lead to misdiagnosis and ineffective treatment, ultimately prolonging the patient’s suffering.
Vertigo & Dizziness Treatment Options: Addressing the Root Causes
Treating vertigo, dizziness, and imbalance requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying causes. The available treatment options include:
1. Vestibular Rehabilitation:
This specialized physical therapy program aims to improve the brain’s ability to compensate for vestibular system dysfunction. Vestibular rehabilitation exercises, such as gaze stabilization, balance training, and canalith repositioning maneuvers, can help patients regain their balance and reduce symptoms. Studies have shown that vestibular rehabilitation can be highly effective in treating various vestibular disorders.
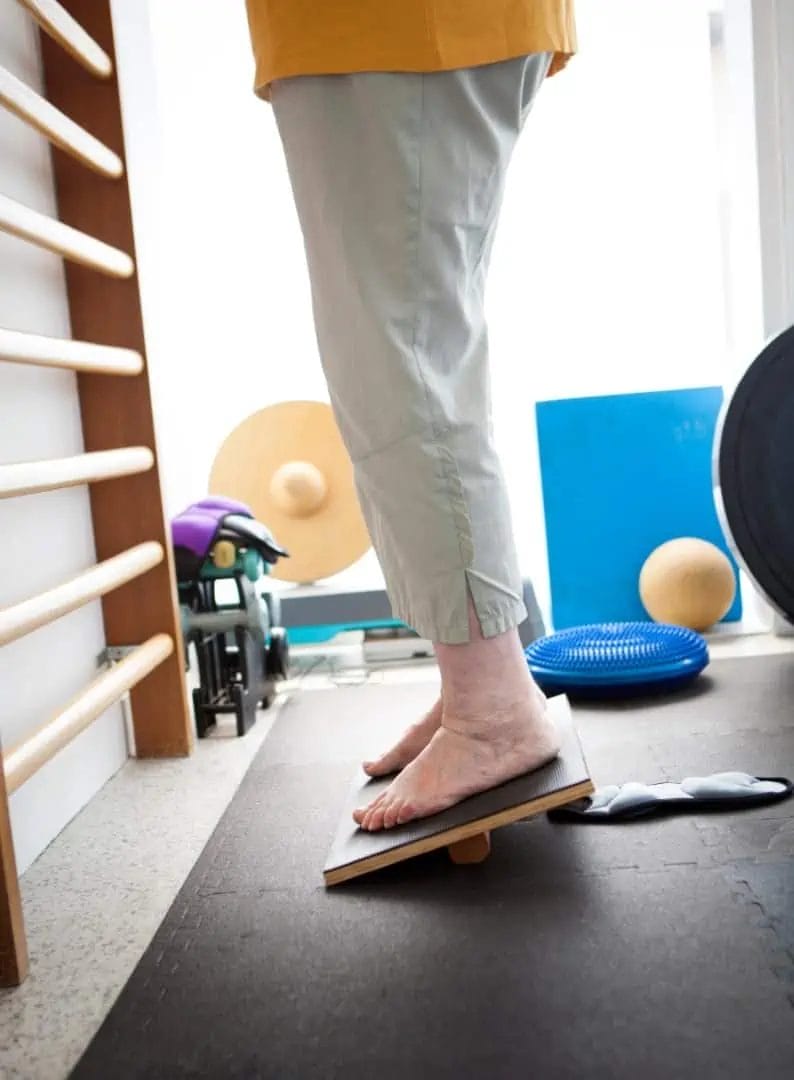

2. Medications:
Certain medications, such as antihistamines, benzodiazepines, and calcium channel blockers, can be used to manage the symptoms of vertigo and dizziness. These medications may provide temporary relief, but they do not address the underlying cause and should be used judiciously.
3. Surgical Interventions:
In some cases, surgical treatment may be necessary, particularly for conditions like Ménière’s disease or vestibular schwannoma. Procedures such as labyrinthectomy, vestibular nerve section, or tumor removal can help alleviate symptoms in select patients.
4. Lifestyle Modifications:
Adjustments to daily activities, such as avoiding sudden head movements, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can also play a role in managing vertigo, dizziness, and imbalance.
It’s important to note that the most effective treatment approach often involves a combination of these options, tailored to the individual patient’s needs and the underlying cause of their symptoms.
Vestibular Disorders and Their Treatment
Vertigo, dizziness, and imbalance can be symptoms of various vestibular disorders, each with its own unique pathophysiology and treatment approach. Some of the common vestibular disorders and their treatments include:
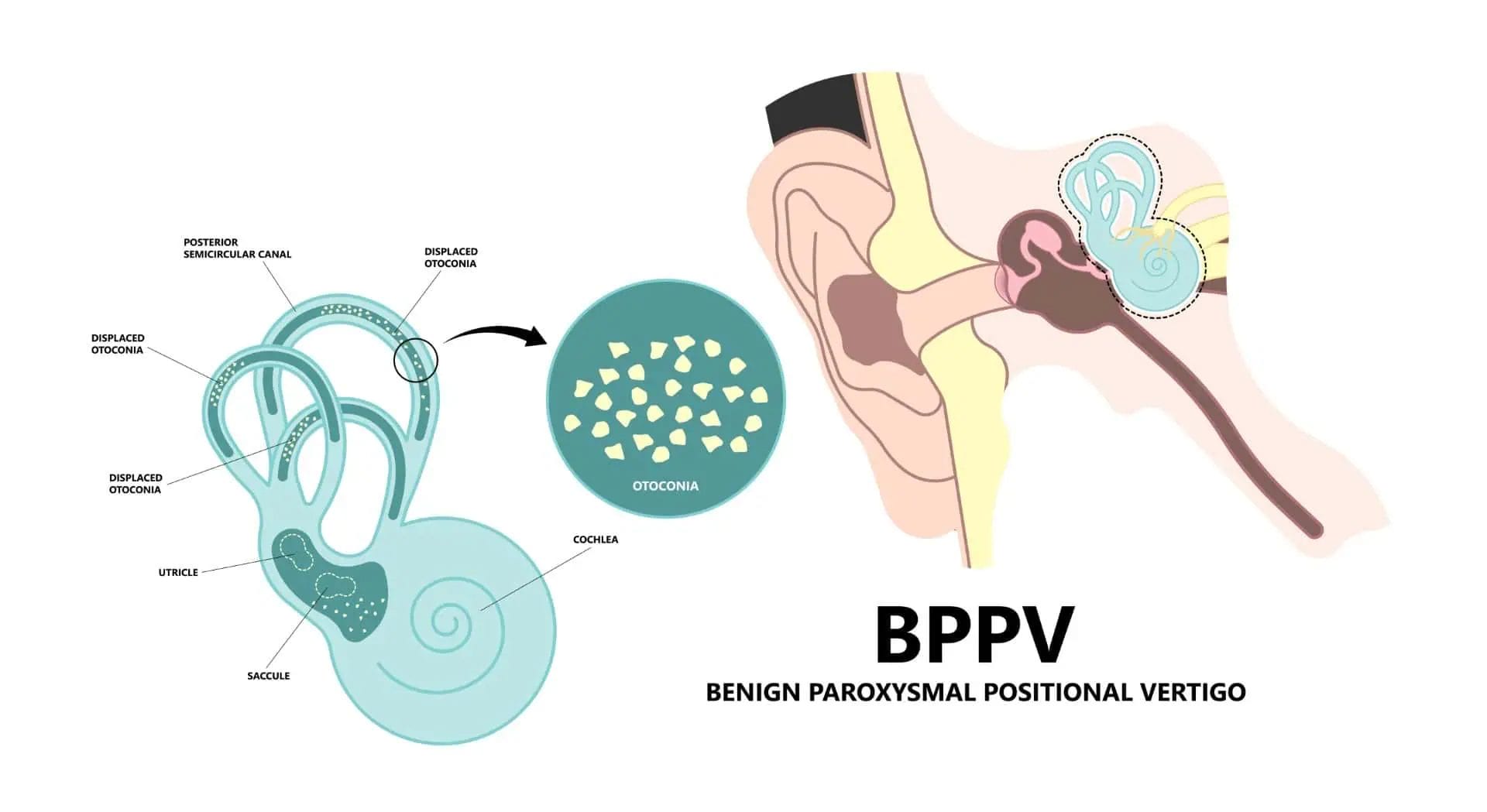
1. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV):
BPPV is caused by the displacement of calcium carbonate crystals (otoconia) within the inner ear, leading to episodes of vertigo triggered by changes in head position.
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is one of the most common causes of vertigo, a sensation of spinning or dizziness. BPPV occurs when tiny calcium crystals (otoconia) become dislodged from their normal position in the inner ear and move into one of the three semicircular canals.
Pathophysiology of BPPV
The inner ear contains three semicircular canals – posterior, anterior, and lateral – that help us maintain balance and orientation. When the otoconia break free and move into these canals, they can stimulate the sensitive nerve endings, causing the sensation of spinning or vertigo when the head is moved in certain positions.
There are two main types of BPPV based on the location of the displaced otoconia:
- Canalolithiasis: The otoconia are free-floating in the semicircular canal, causing vertigo when the head is moved.
- Cupulolithiasis: The otoconia are attached to the cupula (a gelatinous structure in the inner ear), causing vertigo when the head is moved.
Types of BPPV
The most common type of BPPV is posterior canal BPPV, which accounts for about 60-90% of cases. The lateral (horizontal) canal and anterior canal BPPV are less common.
- Posterior Canal BPPV: This is the most frequent type, where the otoconia are displaced into the posterior semicircular canal.
- Lateral Canal BPPV: In this type, the otoconia are displaced into the lateral semicircular canal. It can be further classified into geotropic (debris in the non-ampullary arm) or apogeotropic (debris in the ampullary arm).
- Anterior Canal BPPV: This is the rarest type, where the otoconia are displaced into the anterior semicircular canal.
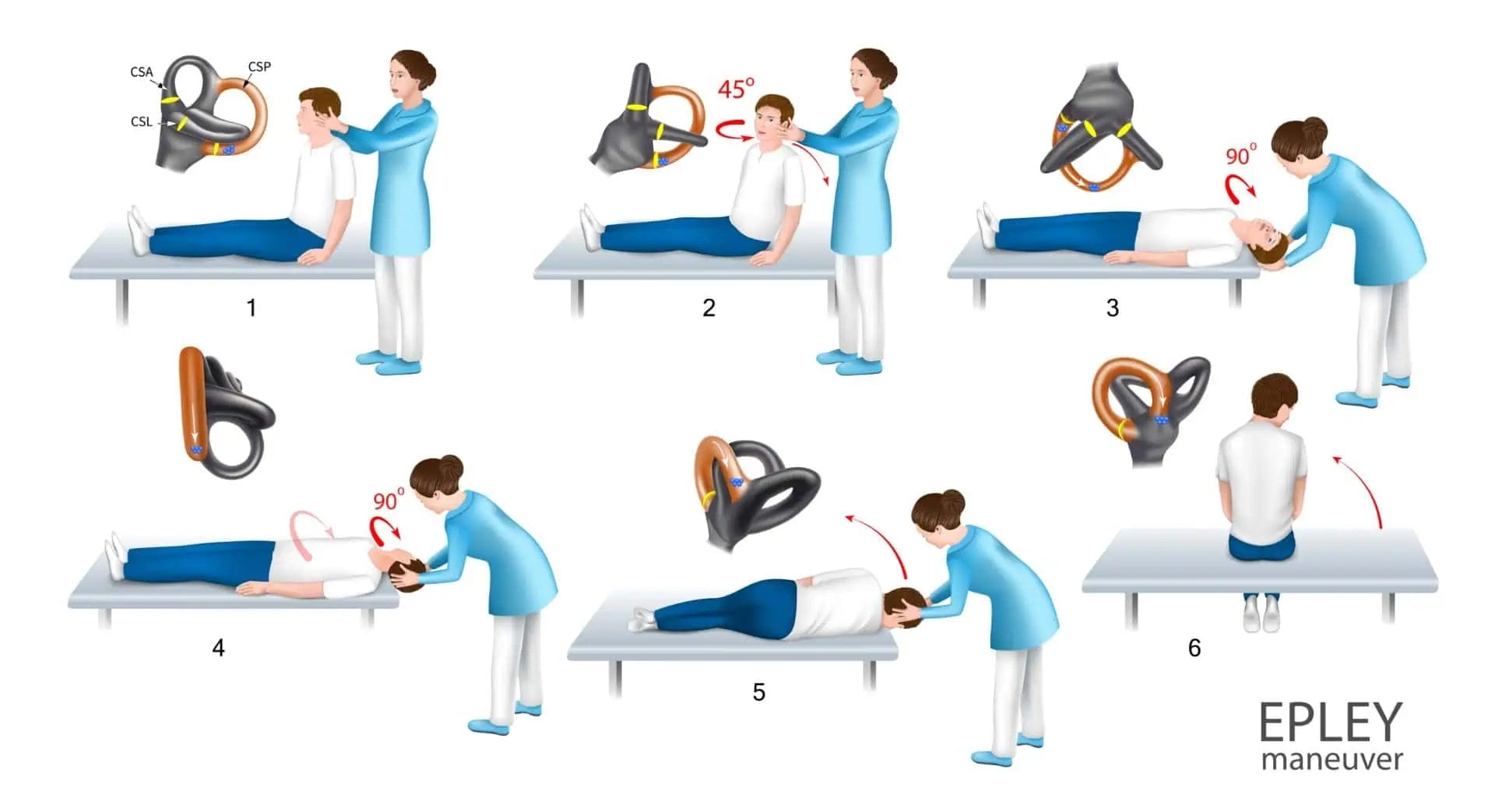
Proper Diagnosis for proper Treatment of BPPV
Proper diagnosis of the type of BPPV and the affected ear is crucial for effective treatment. The key is to perform specific positional tests, such as the Dix-Hallpike test for posterior and anterior canal BPPV, and the supine roll test for lateral canal BPPV.
Treatment for BPPV:
Once the type and affected ear are identified, the appropriate treatment can be administered. The most common treatment is a series of head movements called canalith repositioning maneuvers, such as the Epley maneuver for posterior canal BPPV or the Gufoni maneuver for lateral canal BPPV. These maneuvers aim to move the displaced otoconia back to their original position in the utricle, where they belong.
It is important to note that proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the successful management of BPPV. Attempting to treat BPPV without first identifying the type and affected ear can lead to ineffective or even worsening of symptoms.
In conclusion, BPPV is a common and treatable cause of vertigo. Understanding the pathophysiology and types of BPPV, as well as the importance of proper diagnosis and targeted treatment, is key to effectively managing this condition and improving the quality of life for those affected. Learn more about BPPV and BPPV treatment.
2. Ménière’s Disease:
Meniere’s disease is a complex and puzzling condition that affects the inner ear, causing a range of debilitating symptoms. As a vestibular professor, I’m here to provide a simple and straightforward explanation of this condition, its underlying causes, and the importance of proper diagnosis and treatment.
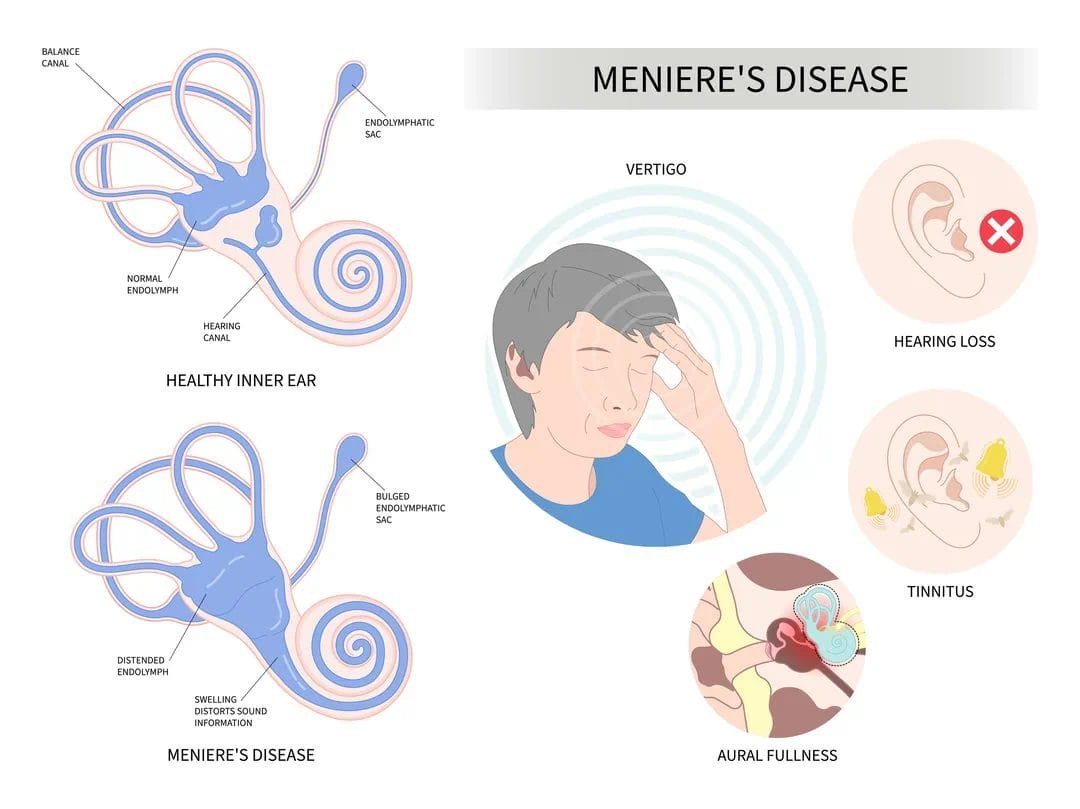
Pathophysiology of Meniere’s Disease:
At the heart of Meniere’s disease is a problem with the fluid balance in the inner ear. The inner ear contains a delicate system of fluid-filled chambers, known as the endolymphatic system. In Meniere’s disease, there is an abnormal accumulation of this fluid, leading to a condition called endolymphatic hydrops. This buildup of fluid puts pressure on the sensitive structures within the inner ear, causing the characteristic symptoms of Meniere’s disease.
The exact cause of this fluid imbalance is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of factors, including genetic predisposition, autoimmune disorders, and even viral infections. Regardless of the underlying cause, the result is the same: a disruption in the normal functioning of the inner ear, leading to the debilitating symptoms of Meniere’s disease.
Symptoms of Meniere’s Disease:
The hallmark symptoms of Meniere’s disease include:
- Vertigo: Sudden, severe episodes of dizziness and a spinning sensation, which can last for minutes to hours.
- Hearing loss: Fluctuating, low-frequency hearing loss, often in one ear.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing sounds in the affected ear.
- Aural fullness: A feeling of pressure or fullness in the affected ear.
These symptoms can come and go, with periods of relative calm followed by sudden, disabling episodes. The unpredictable nature of Meniere’s disease can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks and activities.
Proper Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosing Meniere’s disease is crucial, as it helps to differentiate it from other inner ear conditions with similar symptoms. A vestibular specialist, will perform a comprehensive evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests.
Once Meniere’s disease is properly diagnosed, the treatment approach can be tailored to the individual’s needs. The primary goals of treatment are to manage the symptoms, prevent further hearing loss, and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Meniere’s Disease Treatment:
Treatment options may include
- Dietary modifications: Reducing salt intake and avoiding certain foods and beverages that may trigger symptoms.
- Medications: Diuretics, anti-vertigo medications, or corticosteroids to help control fluid balance and reduce inflammation.
- Intratympanic injections: Delivering medications directly into the middle ear to target the affected inner ear.
- Vestibular Rehabilitation: A brain retraining option to overcome any residual symptoms and to improve balance, is essential for all Meniere’s Disease patients.
- Surgical interventions: In severe or refractory cases, surgical procedures may be considered to reduce fluid buildup or improve inner ear function.
The key to effective treatment is the proper diagnosis of the type and the affected ear. This information is crucial in guiding the most appropriate treatment plan, as Meniere’s disease can present differently in each individual.
In conclusion, Meniere’s disease is a complex and challenging condition, but with proper diagnosis and a tailored treatment approach, many individuals can find relief from their symptoms and improve their quality of life. If you or a loved one are experiencing the symptoms of Meniere’s disease, it’s important to seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
3. Vestibular Neuritis:
Vestibular neuritis is a disorder that affects the inner ear and can cause significant disruption to your balance and equilibrium.
Pathophysiology of Vestibular Neuritis:
Vestibular neuritis is caused by an inflammation or infection of the vestibular nerve, which is responsible for transmitting information about balance and movement from the inner ear to the brain. This inflammation can be triggered by a viral infection, such as the common cold or flu virus. When the vestibular nerve becomes inflamed, it can no longer properly transmit information to the brain, leading to a sudden onset of dizziness, vertigo, and loss of balance.
The symptoms of vestibular neuritis can be quite debilitating, with patients often experiencing a spinning or whirling sensation, nausea, and difficulty standing or walking. In some cases, the dizziness may be accompanied by hearing loss or ringing in the ear.
Proper Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosing vestibular neuritis is crucial, as it can be easily confused with other conditions that cause similar symptoms, such as Ménière’s disease or a stroke. Your healthcare provider will likely perform a series of tests, including a physical examination, balance tests, and imaging studies, to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms.
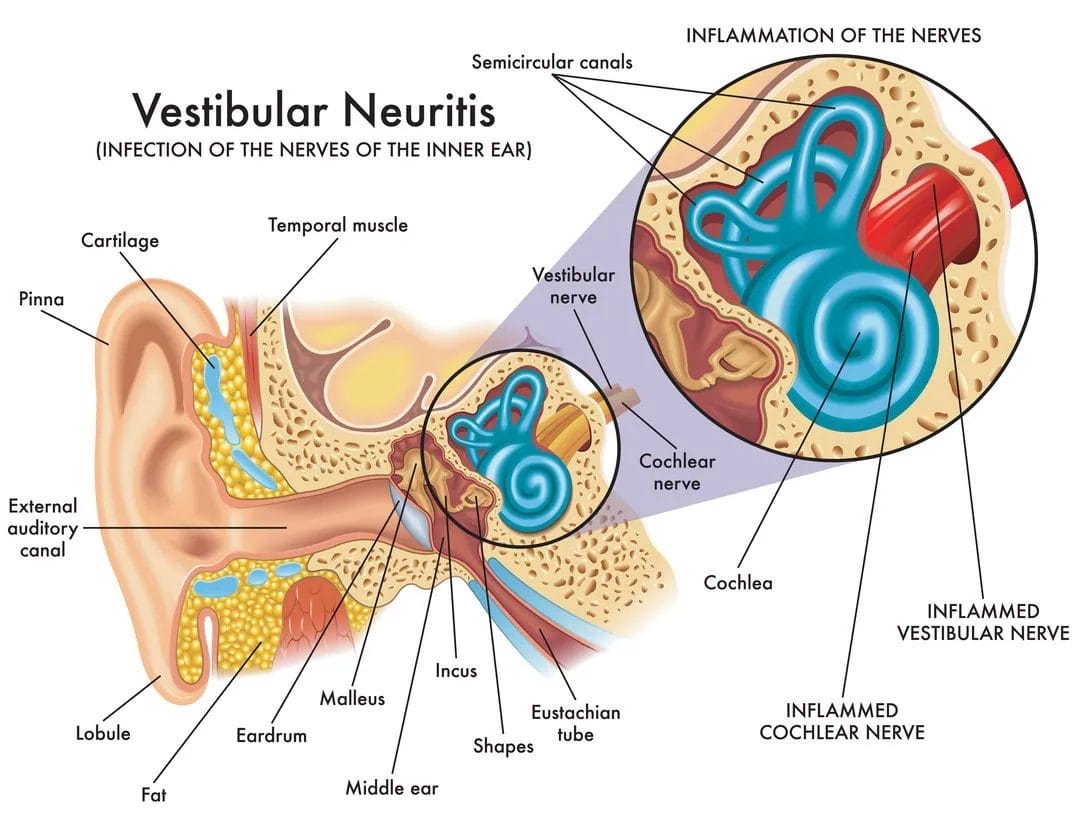
Vestibular Neuritis Treatment:
Once a diagnosis of vestibular neuritis is made, the primary goal of treatment is to manage the symptoms and help the brain adapt to the disruption in vestibular function. This may involve:
- Medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to reduce inflammation, relieve nausea, and alleviate the symptoms of dizziness and vertigo. It is important to note that prolonged usage of medications can adversely affect the condition, medications should only be used at initial stages to alleviate the symptoms, Vestibular Rehabilitation is an effective treatment.
- Vestibular rehabilitation: A specialized physical therapy program that helps retrain the brain to compensate for the disruption in vestibular function. This can involve exercises that challenge your balance and coordination, as well as techniques to help reduce the intensity of your symptoms.
- Lifestyle modifications: Making adjustments to your daily activities, such as avoiding sudden head movements or limiting your exposure to bright lights or loud noises, can help minimize the impact of vestibular neuritis on your daily life.
It’s important to note that the recovery process can vary from person to person, and some individuals may experience persistent symptoms even after treatment, especially if they are on prolonged medications. However, with proper diagnosis and management, most people with vestibular neuritis can expect to make a full recovery over time.
If you or a loved one are experiencing sudden, unexplained dizziness or vertigo, don’t hesitate to seek vestibular specialist attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing the symptoms of vestibular neuritis and minimizing its impact on your daily life.
4. Vestibular Migraine:
Vestibular Migraine (VM) is a condition that affects the balance and coordination system in the inner ear, causing episodes of dizziness or vertigo (a spinning sensation). This condition is often misunderstood and underdiagnosed, but it is actually quite common, affecting around 1-3% of the general population.
Pathophysiology of Vestibular Migraine:
The exact cause of VM is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to changes in the brain and inner ear that occur during a migraine attack. During a migraine, the blood vessels in the brain can become inflamed and irritated, which can then affect the balance and coordination centers in the inner ear. This can lead to the sudden onset of dizziness, vertigo, nausea, and other symptoms.
Treating Vestibular Migraine:
Proper diagnosis is key when it comes to treating VM. Your doctor will need to rule out other potential causes of your dizziness, such as Ménière’s disease or benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), before diagnosing VM. This may involve a variety of tests, including hearing tests, balance tests, and imaging scans.
Once VM is diagnosed, there are several treatment options available:
- Lifestyle changes: Identifying and avoiding potential migraine triggers, such as certain foods, stress, or hormonal changes, can help reduce the frequency and severity of VM episodes.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications to prevent or treat the migraine attacks, such as anti-seizure drugs, antidepressants, or beta-blockers.
- Vestibular rehabilitation: This type of physical therapy can help improve balance and coordination, and can be particularly helpful for managing the dizziness and vertigo associated with VM.
- Complementary therapies: Some people find relief from VM symptoms through alternative treatments, such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, or biofeedback.
It’s important to work closely with your doctor to find the right treatment plan for you. With the right approach, many people with VM are able to manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
5. Persistent Postural-Perceptual Dizziness (PPPD):
PPPD is a chronic functional vestibular disorder characterized by persistent dizziness or unsteadiness, often triggered by upright posture, movement, or exposure to complex visual stimuli.
PPPD Treatment:
The treatment for PPPD typically includes a combination of vestibular rehabilitation, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and, in some cases, medication.
It’s important to note that the specific treatment approach for each vestibular disorder may vary depending on the individual patient’s symptoms, medical history, and response to treatment. A comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional is essential to ensure the correct diagnosis and the most appropriate treatment plan.
The Importance of Proper Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial in the management of vertigo, dizziness, and imbalance. Many patients often undergo multiple consultations with various healthcare providers, such as general practitioners, ENT specialists, or neurologists, before receiving a proper diagnosis. This can lead to a delay in appropriate treatment and a prolonged period of suffering for the patient.
One of the common challenges in diagnosing vestibular disorders is the overlap of symptoms between different conditions. For example, both BPPV and vestibular migraine can present with episodes of vertigo, making it difficult to differentiate between the two without a comprehensive evaluation. Misdiagnosis can result in the prescription of inappropriate medications or the failure to address the underlying cause of the patient’s symptoms.
In recent years, the recognition of a condition called Persistent Postural-Perceptual Dizziness (PPPD) has highlighted the importance of a thorough diagnostic approach. PPPD is a chronic functional vestibular disorder that can be easily overlooked or misdiagnosed, leading to ineffective treatment and a worsening of the patient’s symptoms.
To ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, healthcare providers should consider a multidisciplinary approach, which may include a combination of medical history, physical examination, vestibular function testing, and, in some cases, neuroimaging. By identifying the underlying cause of the patient’s symptoms, healthcare providers can develop a targeted treatment plan that addresses the root of the problem, ultimately improving the patient’s quality of life.
Conclusion: Empowering Patients through Awareness and Proper Care
Vertigo, dizziness, and imbalance are complex and often misunderstood symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s daily life. By understanding the differences between these symptoms and the various vestibular disorders that can cause them, patients can advocate for themselves and seek the appropriate medical care.
Through increased awareness and access to comprehensive diagnostic and treatment options, patients can find relief and regain their quality of life. Healthcare providers should strive to provide a multidisciplinary approach, combining medical expertise, vestibular rehabilitation, and patient education to ensure the best possible outcomes for those suffering from these debilitating symptoms.
Remember, proper diagnosis and tailored treatment can make a significant difference, even for long-standing vertigo, dizziness, or imbalance. By empowering patients and promoting a better understanding of these conditions, we can work together to improve the lives of those affected by these often-overlooked vestibular disorders.